
Table of Content
ToggleIntroduction
Teenagers and their parents may find it worrying when they experience hair loss during adolescence. This involves hair thinning or loss during a critical period of physical and emotional development for young people.
Adolescent hair loss can be brought on by a number of things, including hormonal fluctuations, dietary deficiencies, stress, and genetic susceptibility. Hormonal changes that occur throughout puberty might impact the hair growth cycle and cause greater thinning or hair loss.
Hair health and growth can be impacted by dietary deficiencies, particularly those related to vitamins such as iron, zinc, and biotin. Emotional strain, resulting from scholastic demands, interpersonal difficulties, or individual problems, may disrupt the body’s regular processes and lead to hair loss.
Hereditary factors are significant since kids who have a family history of hair loss are more likely to experience comparable issues. Hair loss can also be brought on by specific drugs or medical disorders like alopecia areata. Teenage hair loss can be treated by modifying lifestyle choices and determining the underlying cause through medical evaluation.
Purpose of the Post
The blog post aims to investigate the reasons behind teenage hair loss and provide workable remedies. It attempts to give a thorough explanation of the causes of teenage hair loss, including hormonal fluctuations, dietary inadequacies, stress, genetics, drugs, and improper hair care.
This article will address the symptoms that parents and teenagers should be aware of, as well as how these variables contribute to hair loss. It will also offer helpful guidance on how to manage teenage hair loss, including dietary suggestions, methods for managing stress, medicinal treatments, and appropriate hair care procedures.In general, the purpose is to provide readers with information and solutions for managing and potentially reversing hair loss in teenagers, thereby improving their general health and well-being.
The Basics of Hair Growth
Hair follicles grow, rest, and shed as part of a continual process known as the hair growth cycle. Each hair follicle experiences independent cycles, which means that not all hairs are in the same phase at the same time. For an understanding of hair growth and hair fall, these stages must be understood.
Stages of Hair Growth
The hair growth cycle includes three main stages:
- Anagen Phase (Growth Phase)
- Catagen Phase (Transitional Phase)
- Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)
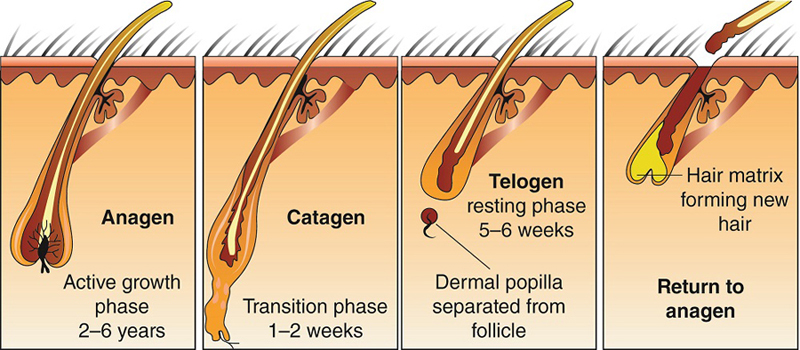
The growth, rest, and shedding phases of individual hair strands are determined by the combination of these stages. Let’s study each phase in depth:
- Anagen Phase (Growth Phase)
The hair follicle’s active growth phase is known as the anagen phase.During this stage:
Duration- The duration of the anagen phase is influenced by a number of factors, including body location and genetics. It usually lasts two to seven years on the scalp.
Activity- New hair cells are actively being produced by the hair follicle, and these cells eventually keratinize to create the hair shaft.
Growth Rate- During the anagen phase, hair grows approximately 1 centimeter every 28 days.
The maximum length that hair can grow depends on how long the anagen phase lasts. At any given time, 85–90% of the hairs on your scalp are in the anagen phase.
- Catagen Phase (Transitional Phase)
Between the anagen and telogen phases comes a phase known as the catagen phase.During this phase:
Duration: This phase lasts around 2 to 3 weeks.
Activity: The hair follicle contracts and separates from the dermal papilla, which is the nutrient-supplying structure at the base of the follicle.
Changes: The hair stops growing and turns into club hair, which is a non-growing hair that hasn’t shed yet.
During the catagen phase, the outer root sheath contracts and connects to the hair roots. This procedure separates the hair strand from its blood supply and the cells that create new hair.
- Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)
The hair development cycle’s resting period is known as the telogen phase.During this phase:
Duration: This period usually lasts 3 to 4 months.
Activity: Telogen is a period of rest for the hair follicle. The hair is not actively developing and is firmly attached in the follicle.
Shedding: At any given time, 10–15% of the hairs on the scalp are in the telogen phase. In order to provide space for future hair development, these hairs are shedding and will eventually fall out.
New Growth: New hair starts to develop in the follicle, pushing out the old hair as the old hair rests and finally sheds.
The telogen phase is a natural component of the hair development cycle that is required for renewal.
Common Causes of Hair Loss in Adolescents

Adolescent hair loss is often brought on by a number of circumstances and can be quite upsetting. These are a few typical reasons:
1.Genetics (Hereditary Hair Loss):
Males and girls can experience pattern hair loss during adolescence due to androgenetic alopecia. It is identified by a progressive thinning of scalp hair.
2.Hormonal Changes:
Temporary hair loss during puberty might be caused by hormonal imbalances. This is especially frequent in girls because progesterone and estrogen fluctuations can have an impact on hair development.
3.Nutritional Deficiencies:
Hair thinning and loss may result from inadequate consumption of vital nutrients such as iron, zinc, vitamins (particularly vitamin D and B vitamins), and proteins.
4.Medical Conditions:
Hair loss can be brought on by illnesses including fungal infections on the scalp, autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, and thyroid problems like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
5.Stress and Emotional Factors:
Anxiety, trauma, and emotional stress can cause telogen effluvium, a disorder in which a large number of hair follicles prematurely enter the resting (telogen) phase and shed their hair.
6.Hair Care Practices:
Overuse of harsh hair care products, tight hairstyles (such braids and ponytails), and chemical or heat styling treatments can all lead to hair damage, breaking, and loss of hair.
7.Medications:
Hair loss is a negative effect of some drugs used to treat depression, acne, and other medical issues.
8.Lifestyle Factors:
Adopting unhealthy lifestyle habits like smoking, binge drinking, and crash dieting can have detrimental effects on general health and exacerbate hair loss.
9.Environmental Factors:
Hair damage and hair loss can be caused by exposure to pollution, chlorine in swimming pools, and harsh weather conditions.
10.Trichotillomania:
This is a psychological disease in which people have an uncontrollable impulse to pull their own hair, resulting in visible hair loss.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider or a dermatologist if an adolescent experiences sudden or excessive hair loss to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Addressing the cause promptly can often prevent further hair loss and promote healthy hair growth.
Identifying Hair Loss in Adolescents

Let’s delve into identifying hair loss in adolescents, including signs and symptoms to look for, and guidance on when to seek help from a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
Signs and Symptoms of Hair Loss in Adolescents
Hair loss in adolescents can present in various ways.Here are some common indications and symptoms to check for:
1.Thinning Hair:
Hair on the scalp gradually thins, with the portion line or the crown being the most obvious places.
2.Bald Spots (Alopecia Areata):
Round or oval spots of hair loss on the scalp that occur suddenly. These areas could be smooth or appear somewhat stubbled.
3.Excessive Shedding (Telogen Effluvium):
Increased hair loss that is frequently observed when brushing, cleaning, or moving fingers through the hair. This may result in general hair thinning.
4.Patches of Broken Hair:
Various lengths of broken hair strands, which suggest that the cause of the breakage is either internal health issues or external injury.
5.Scalp Redness or Scaling:
There may be scaling, redness, or irritation of the scalp, particularly in situations of infections or disorders of the scalp.
6.Changes in Hair Texture:
Alterations in hair texture, such as brittleness, dryness, or exceptional coarseness.
7.Changes in Hairline:
A receding hairline or changes in the shape of the hairline may be a sign of genetic or hormonal issues.
8.Psychological and Emotional Signs:
Teens may exhibit symptoms of tension, worry, or low self-esteem as a result of changes in their hairstyle.
When to Seek Help

It’s important to seek medical advice if an adolescent experiences any of the following concerning signs or symptoms of hair loss:
1.Sudden or Excessive Hair Loss
2.Visible Bald Patches
3.Signs of Infection on the Scalp
4.Changes in Hair Texture or Color
5.Family History of Hair Loss
6.Significant Psychological Impact
7.Underlying Medical Conditions
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider or Dermatologist- It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider or dermatologist if any of the above signs or symptoms are observed.
Treatment and Management- Treatment for hair loss in adolescents depends on the underlying cause and may include:
1.Medications: Prescribed to treat conditions such as alopecia areata or hormonal imbalances.
2.Topical Treatments:For conditions like fungal infections or to promote hair growth.
3.Lifestyle Changes:Advised to improve overall health and prevent further hair loss.
4.Psychological Support: Counseling or support to address emotional distress related to hair loss.
Healthy hair growth and the prevention of more hair loss can frequently be achieved with early intervention and the right medical care. As a result, it’s critical that teens who detect symptoms of hair loss seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Solutions and Treatments for Hair Loss

1.Healthy Diet
To maintain healthy hair development, a diet rich in necessary nutrients and well-balanced is essential. The following are some essential nutrients that are vital to the health of hair, along with sources:
- Protein: Protein is the main component of hair. Lean meats, seafood, eggs, beans, and legumes are examples of sources.
- Iron: Hair loss may be caused by an iron shortage. Lentils, red meat, spinach, and fortified cereals are good sources.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in almonds, avocados, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and fish like salmon.
- Vitamins:For healthy hair, vitamins A, C, D, and E are crucial. Fruits, veggies, dairy products, and fortified cereals are examples of sources.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7):present in whole grains, eggs, nuts, and cauliflower. Supplementing with biotin could also be an option.

2.Stress Management
Hair loss may be increased by ongoing stress. Among the methods for stress management are:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Stress can be decreased by engaging in activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity enhances general health and lowers stress.
- Counseling or Therapy: To properly handle stress and anxiety, seek professional assistance.
3.Medical Treatments
Depending on the reason of hair loss, medical therapies may be advised:
- Topical Treatments: Minoxidil (Rogaine)- Over-the-counter topical gel or foam that can stop more hair loss and encourage hair growth
- Oral Medications: Finasteride (Propecia)-Men can take a prescription medicine to help reduce DHT levels, a hormone linked to hair loss.
- Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions: Treating illnesses that may be causing hair loss, such as thyroid issues or infections on the scalp

4.Proper Hair Care
Gentle hair care techniques can reduce damage and encourage strong, healthy hair growth.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Use of bleaches, hair colors, and styling products with harsh chemicals should be limited.
- Protective Hairstyles: To stop hair breakage, stay away from hairstyles that tug on the hair, such as tight braids and ponytails.
5.Supplements
Supplements can promote healthy hair, particularly in cases of deficiency:
- Biotin: Strengthens the nails and hair.
- Iron: Important in reducing hair loss caused by iron deficient anemia.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promote healthy hair development and a scalp.

6.Professional Treatments
Advanced treatments may be considered for more severe or persistent hair loss:
- Laser Therapy (Low-Level Laser Therapy, LLLT): Encourages the growth of hair by stimulating hair follicles.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Involves stimulating hair follicles by injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: 1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)- involves implanting scalp strips containing hair follicles from a donor area into areas experiencing baldness
2.Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)- Involves taking individual hair follicles out of the donor region and putting them in the recipient.
Emotional and Psychological Support

Support, both emotional and psychological, is essential for people struggling with a range of life’s obstacles, such as illnesses, stress, grief, and mental illnesses. Offering complete support can enhance resilience, general well-being, and quality of life.
The term “emotional and psychological support” describes a variety of programs and services intended to assist people in overcoming psychological difficulties, mental health issues, and distress. Support groups, loved ones, medical professionals, and different therapeutic approaches can all provide this kind of assistance.
A wide range of services and interventions are included in the category of emotional and psychological support, with the goal of supporting people in overcoming emotional discomfort and mental health issues. Professional therapy and counseling, which includes services from licensed counselors, psychologists, and psychiatrists, offer systematic, research-based methods to treat a range of mental health issues.Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one such approach.
Peer-led focused on particular issues such as addiction, chronic illness, or sadness, support groups offer collective support, promoting a feeling of acceptance and common ground. Crisis hotlines and intervention services are vital for preventing suicide and providing emergency mental health care because they provide quick aid and emotional support to people in times of acute distress. People can now access mental health treatments more easily because of the development of telehealth and online therapy platforms, which provide video, phone, or chat sessions for support.
Furthermore, it’s commonly known that mindfulness and meditation techniques may reduce stress and enhance emotional control. Psychotropic medicine under the supervision of psychiatrists can be crucial for people suffering from depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Emotional well-being is further enhanced by supportive workplace practices, community services, and open communication and active listening within families. Self-care routines, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, enough sleep, and hobbies, are essential to preserving mental wellness.
It is necessary to tackle the stigma attached to mental health concerns by means of education, advocacy, and awareness-raising in order to motivate people to pursue the necessary assistance. All things considered, the complexity of emotional and psychological support highlights the significance of a thorough, integrated approach to mental health treatment.
Conclusion

In conclusion, a variety of genetic, hormonal, medical, dietary, and lifestyle variables can contribute to hair loss in teens. Hereditary hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, can start in adolescence and be impacted by family history. Hair loss can be made worse by puberty-related hormonal changes, especially the rise in androgens. Adolescent hair loss is also greatly influenced by medical diseases including thyroid issues and alopecia areata.
Hair health can be harmed by nutritional deficits, particularly those involving vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and biotin. Additionally, telogen effluvium—a condition where stress causes hair to prematurely enter the shedding phase—can be brought on by the increased stress and psychological difficulties that are typical of adolescence.
Teenage hair loss can be addressed by treating underlying medical disorders with the proper medical interventions, consuming a balanced diet full of important nutrients, and implementing stress-reduction strategies like frequent exercise and mindfulness.
Topical medications like minoxidil may be helpful in promoting hair growth, and mild hair care techniques like staying away from strong chemicals and tense hairstyles can stop more damage. Seeking advice from a dermatologist or healthcare professional is crucial for precise diagnosis and customized treatment regimens, guaranteeing efficient handling and reduction of teenage hair loss.
A Balanced Lifestyle for Overall Well-Being

To be well-rounded, one must lead a balanced lifestyle that includes mental, emotional, and physical wellness.
1.Nutritious Diet- A balanced diet is vital for good health because it gives the body the nutrients it needs to function at its best, promoting physical health by keeping bones, muscles, and organs in good condition, and strengthening the immune system to fight against illnesses.
By promoting brain function and mood stability, it improves mental health and aids in the prevention of chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
A balanced diet is also essential for children’s and adolescents’ healthy growth and development, helps them maintain a healthy weight, and gives them continuous energy and strength. All things considered, lifespan and quality of life are greatly increased by making a nutritious diet a priority.
2.Regular Physical Activity- It is vital to engage in regular physical activity to preserve general health and wellbeing. It lowers the chance of chronic illnesses including obesity, diabetes, and hypertension; it strengthens the heart and increases blood circulation; it promotes mental health by lowering stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms.
Frequent exercise improves energy levels, sleep quality, and muscle strength, flexibility, and endurance. In addition, exercise promotes strong bones and joints, helps people maintain a healthy weight, and lengthens and enhances quality of life overall. People can greatly improve their physical and mental health by including regular physical activity into their daily routines.
3.Adequate Sleep- Getting enough sleep is essential for preserving general health and wellbeing. The body renews and restores itself when we sleep, promoting mental clarity, emotional stability, and physical well-being.
Sleep improves cognitive function, focus, and productivity and is essential for helping memories and learning stick. Because it helps to balance hormones and neurotransmitters, getting enough sleep is also crucial for controlling mood and emotions. Moreover, getting enough sleep boosts immunity and strengthens the body’s defenses against illnesses and infections.
Conversely, there is a correlation between prolonged sleep deprivation and a higher risk of a number of illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and mental health issues. Thus, for general health and effective functioning, getting enough good sleep is crucial.
4.Stress Management- Managing stress is essential to preserving general health and well-being. Good stress management strategies lessen the negative consequences of ongoing stress on one’s physical and mental well-being while also assisting people in overcoming obstacles in their daily lives.
Deep breathing exercises, frequent physical activity, and mindfulness meditation are among the techniques that can lower cortisol levels, reduce anxiety, and enhance mood. Stress can also be reduced by leading a balanced lifestyle that includes social support networks, a nutritious diet, and enough sleep. People can strengthen their resilience, become better at handling stress, and advance their long-term health and well-being by routinely practicing stress management practices.
5.Avoiding Harmful Habits- Staying away from bad habits is essential to preserving general health and wellbeing. These behaviors may be detrimental to one’s emotional, mental, and physical well-being. Examples include abstaining from excessive alcohol use, which can harm the liver and impair judgment in addition to causing addiction.
Heart disease, respiratory disorders, and lung cancer are all markedly increased by tobacco use. In addition to being bad for the body, using illegal drugs can cause relationship problems and legal problems.
Furthermore, it’s critical to utilize technology in moderation because too much screen time can negatively impact social connections, mental health, and the quality of sleep. People can safeguard their health, enhance their quality of life, and lower their chance of contracting chronic illnesses and other health issues by abstaining from these bad habits.
People can live a happy and healthy life by eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, getting enough sleep, handling stress well, building social networks, attending to their mental health, and abstaining from bad habits. This all-encompassing strategy encourages longevity and resilience against a range of health issues in addition to improving quality of life.
Hormonal fluctuations, dietary inadequacies, genetic susceptibility (androgenetic alopecia), medical diseases (such as thyroid issues or alopecia areata), stress, specific drugs, and improper hair care practices are among the common causes.
While some hair loss in teenagers is natural, excessive hair loss can be concerning and may be brought on by underlying medical conditions or outside influences. Finding and addressing the problem is important.
Hormonal changes that occur throughout puberty might affect the cycles of hair growth. For example, fluctuations in the levels of the hormones androgen and estrogen might result in temporary hair loss or thinning.
In reality, excessive stress can cause telogen effluvium, a condition in which stress forces hair follicles to enter the resting (telogen) phase earlier than normal, resulting in greater shedding. in temporary hair loss or thinning.
Because iron, zinc, vitamin D, and protein are necessary for healthy hair growth, deficiencies in these nutrients can cause hair thinning and loss.

I appreciate you taking the time to read! I hope this blog post about adolescent hair loss was useful to you. Please leave a comment below if you have any questions, experiences, or advice of your own. Remember to forward this article to friends and family who could find it useful. Make sure to follow us on social media and on our blog for further updates and health advice. Your participation aids us in producing more insightful material for you. We eagerly await your feedback!
STAY HAPPY AND HEALTHY!
Great explanation